PEM (PROTON–EXCHANGE MEMBRANE TECHNOLOGY) FEATURES AND ADVANTAGES
Instead of an aggressive alkali solution, a solid polymer membrane with proton conductivity is used as an electrolyte
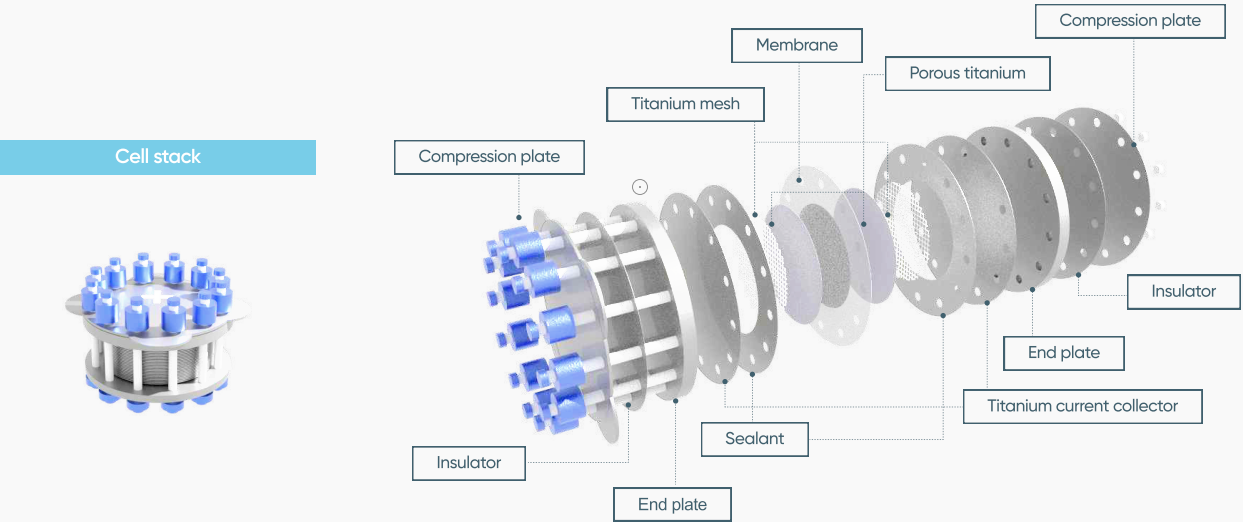
PEM VS ALKALINE ELECTROLYZERS
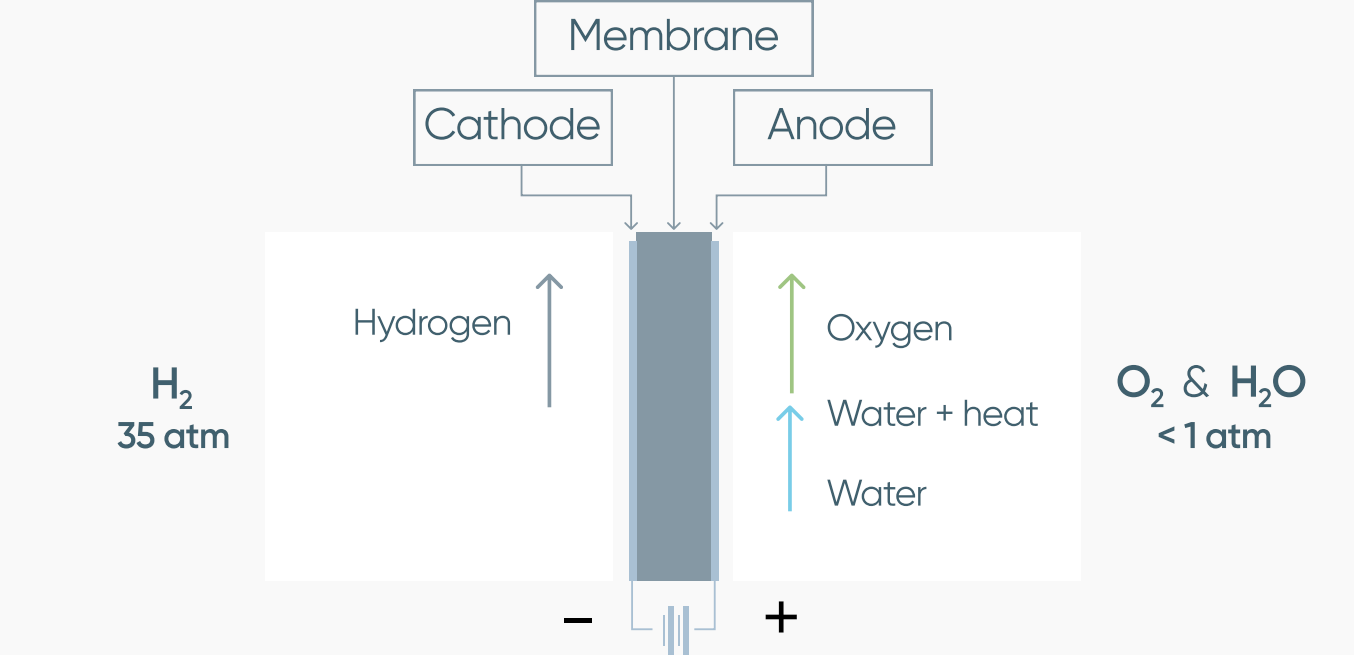
PEM - ELECTROLYZERS
NOT AGRESSIVE, EASY, SAFE
- The only liquid is water
- NO corrosion
- The system works perfectly for many years
- Very easy to maintain
- The only impurity is water vapour (ppm)
- Impossibility of oxygen entering hydrogen
- Membrane is gas-tight — no hydrogen in oxygen
- Low pressure oxygen — no risks associated with pressurised oxygen
- Quick start and stop at any time
- Operation at 0-100% capacity automatically
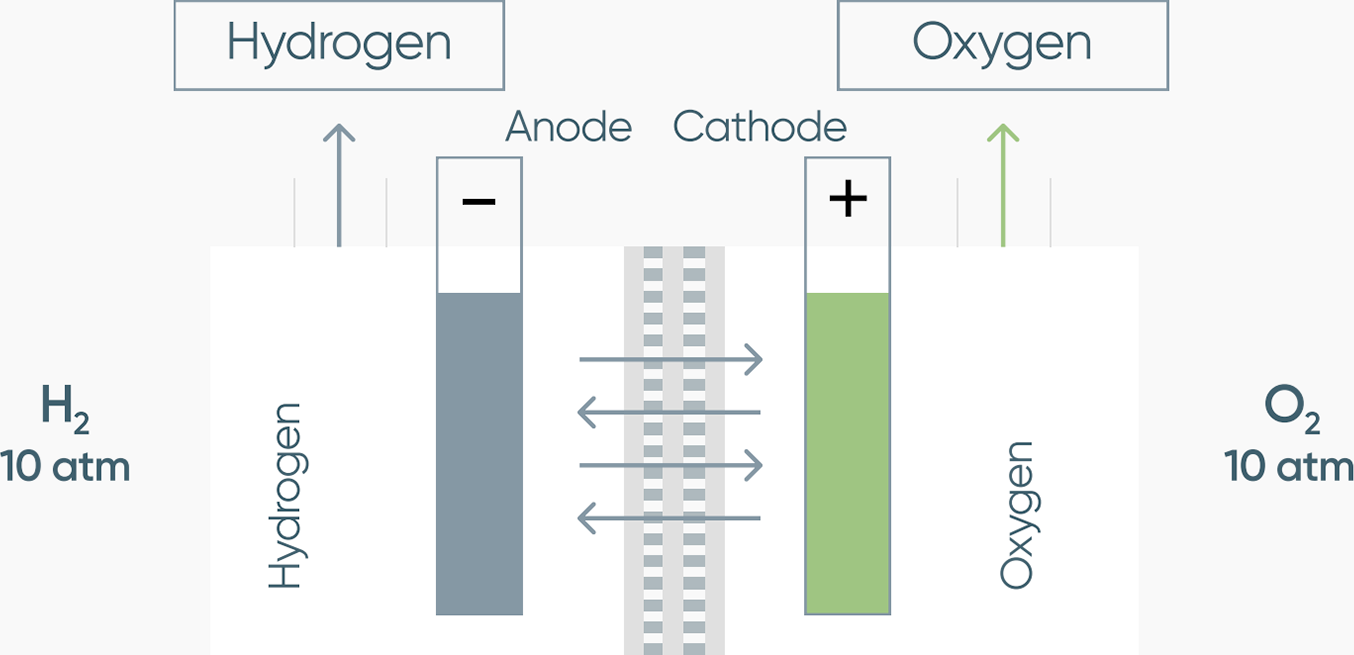
ALKALINE ELECTROLYZERS
AGRESSIVE, DIFFICULT TO REPAIR, NEED FOR OXYGEN MONITORING
- Filled with KOH alkali and operates at 80 C
- High corrosion + pressure LEADS TO risk of failure
- Loss of alkali — needs to be refilled
- Difficult to maintain (system draining)
- Repairs becomes more expensive every year
- Hydrogen contains alkali impurities
- Special clothing and facilities
- Continuous pressure balance
- High hydrogen content in oxygen
- High oxygen content in hydrogen
- Need to monitor pressure balance
- Oxygen at 10 atm next to hydrogen at 10 atm is a risk Nitrogen purging
- Difficult shutdown procedureShutdowns reduce service life


